Federal Budget 2023 … Press the Snooze Button
As promised, there would be nothing much in this year’s budget for fear of stimulating inflation. The federal government faces a challenging fiscal environment and a weakening economy. Ottawa promised it would err on the side of restraint. Instead, Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland announced a $43 billion increase in net new government spending over six years. The new expenditures focus on bolstering the rickety healthcare system, keeping up with the US on new clean-technology incentives, and helping low-income Canadians to deal with rising prices and a slower economy.
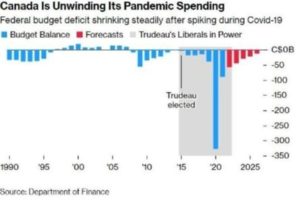
Tax revenues are expected to slow with the weaker economy. The result is a much higher deficit each year through 2028 and no prospect of a balanced budget over the five-year horizon.
The budget outlines significant increases to healthcare spending, including more cash for provincial governments announced earlier this year and a $13-billion dental-care plan that Trudeau’s Liberals promised in exchange for support in parliament from the New Democratic Party.
Freeland is also announcing substantial new green incentive programs to compete with the Inflation Reduction Act signed into US law last year by President Joe Biden. The most significant new subsidy in the budget is an investment tax credit for clean electricity producers. Still, it also includes credits for carbon capture systems, hydrogen production, and clean-energy manufacturing.
The budget promises $31.3 billion in new healthcare spending and $20.9 billion in new green incentive spending by 2028. On top of that is $4.5 billion in affordability measures, half of which is for an extension of a sales tax credit for low-income Canadians.
The spending is partially offset by tax increases on financial institutions and wealthy Canadians and a pledge to reduce government spending on travel and outside consultants. Freeland is planning to raise billions of dollars from banks and insurance companies by changing the tax rules for dividends they get from Canadian firms. The new tax will apply to shares held as mark-to-market assets, not dividends paid from one subsidiary to another.
Wealthy Canadians pay the alternative minimum or regular tax, whichever is higher. The government announced in the budget that it is increasing the alternative minimum rate to 20.5 percent from 15 percent starting in 2024. Ottawa is also imposing new limits on many exemptions, deductions and credits that apply under the system beginning in 2024.
“We’re making sure the very wealthy and our biggest corporations pay their fair share of taxes, so we can afford to keep taxes low for middle-class families,” Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland said in the prepared text of her remarks.
Canada’s debt-to-GDP ratio will worsen next year, despite the government’s reliance on this measure as a fiscal anchor. Debt-to-GDP will rise from 42.4% to 43.5% next year and is projected to decline very slowly over the next five years.
Not Much for Affordable Housing
The budget included a laundry list of measures the federal government has taken to make housing more affordable for Canadians.
Budget 2023 announces the government’s intention to support the reallocation of funding from the National Housing Co-Investment Fund’s repair stream to its new construction stream, as needed, to boost the construction of new affordable homes for the Canadians who need them most.
But there was one initiative tucked away in a Backgrounder entitled “An Affordable Place to Call Home.” I am quoting this directly from the budget:
A Code of Conduct to Protect Canadians with Existing Mortgages
“Elevated interest rates have made it harder for some Canadians to make their mortgage payments, particularly for those with variable rate mortgages.
- That is why the federal government, through the Financial Consumer Agency of Canada, is publishing a guideline to protect Canadians with mortgages who are facing exceptional circumstances. Specifically, the government is taking steps to ensure that federally regulated financial institutions provide Canadians with fair and equitable access to relief measures that are appropriate for the circumstances they are facing, including by extending amortizations, adjusting payment schedules, or authorizing lump-sum payments. Existing mortgage regulations may also allow lenders to provide a temporary mortgage amortization extension—even past 25 years.
This guideline will ensure that Canadians are treated fairly and have equitable access to relief, without facing unnecessary penalties, internal bank fees, or interest charges, which will help more Canadians afford the impact of elevated interest rates.”
We will see what OSFI has to say about this, as the details are always of paramount importance. OSFI is scheduled to announce potential changes to banking regulation to reduce bank risk. We’ve heard a lot about banking risks in recent weeks.
The budget also reduced the legal limit on interest rates. The government intends to lower the criminal rate of interest from 47% (annual percentage rate) to 35%. According to the law firm Cassels, “’Interest’ is defined broadly under the Code and includes all charges and expenses in any form, including fees, fines, penalties, and commissions.”
Bottom Line
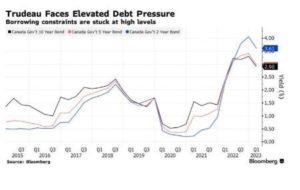
While this was not one of the more exciting budgets, it is important that our debt-to-GDP ratio is low in comparison to other G-7 countries. It is good news that Ottawa recognizes the financial burdens facing homeowners with VRMs. If the banks can extend remaining amortizations when borrowers renew, the pressure on their pocketbooks will be markedly lower.
Dr. Sherry Cooper | Chief Economist, Dominion Lending Centres

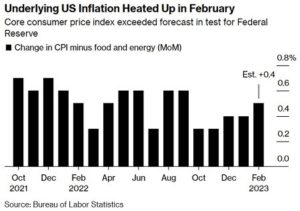
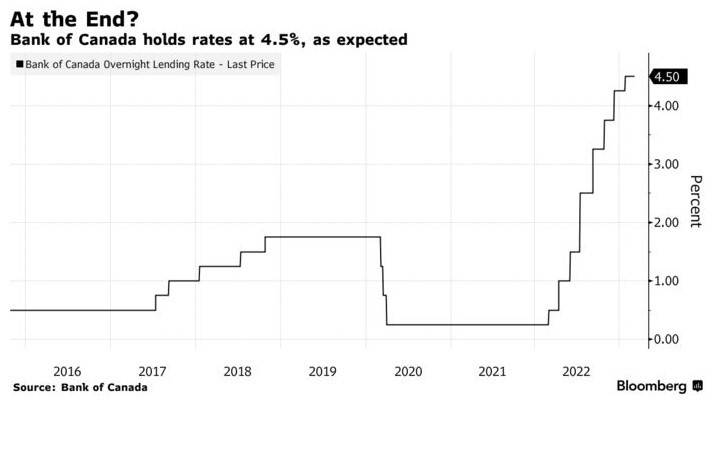
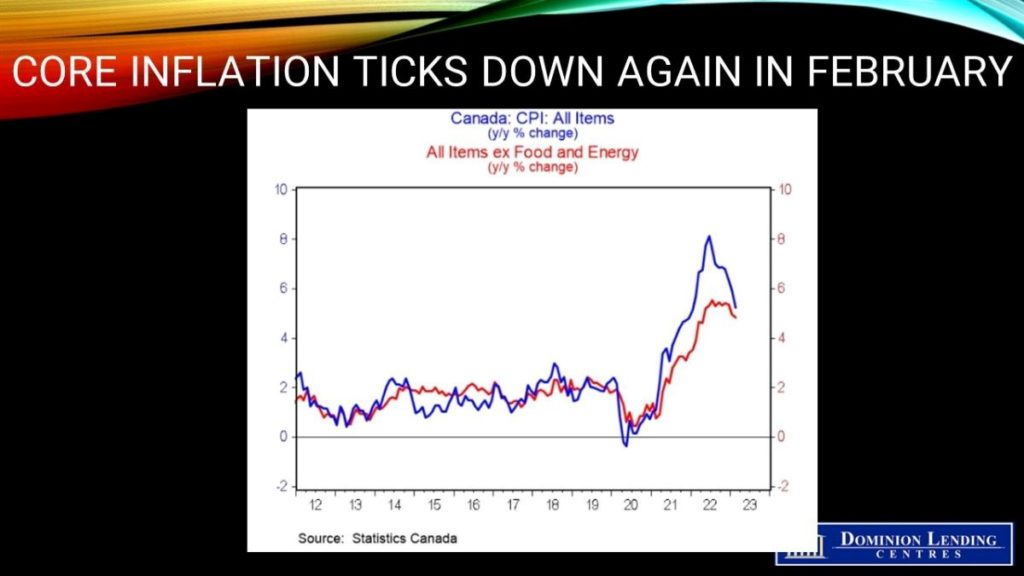
 Further Decline in Inflation in February Will Keep the Bank of Canada on Hold in April
Further Decline in Inflation in February Will Keep the Bank of Canada on Hold in April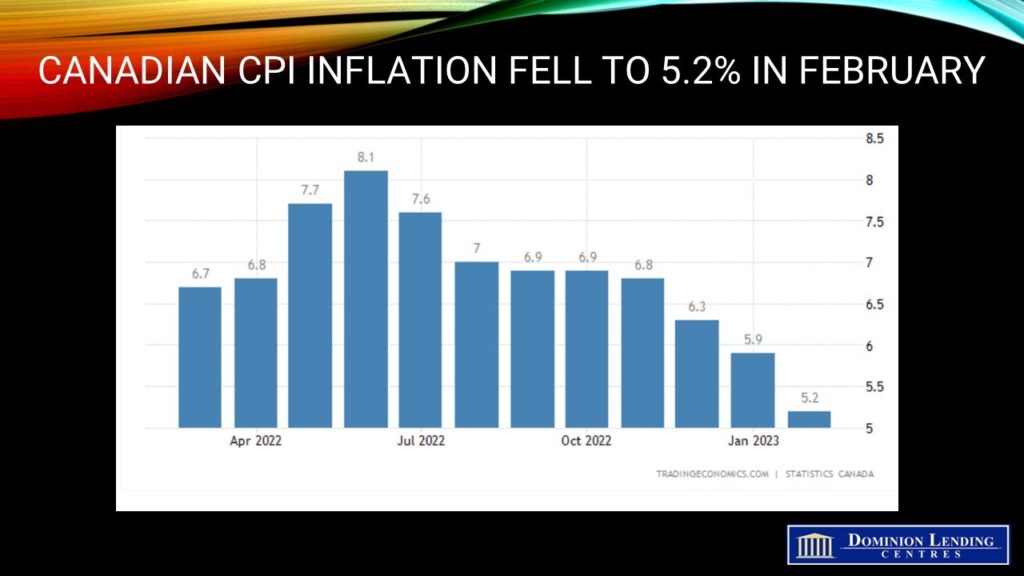
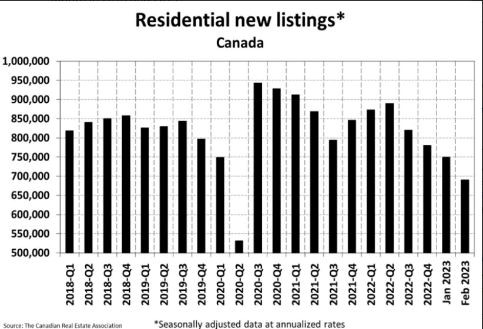
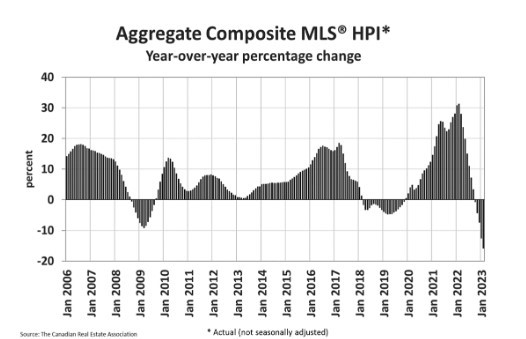
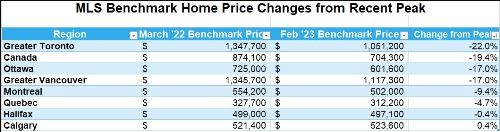
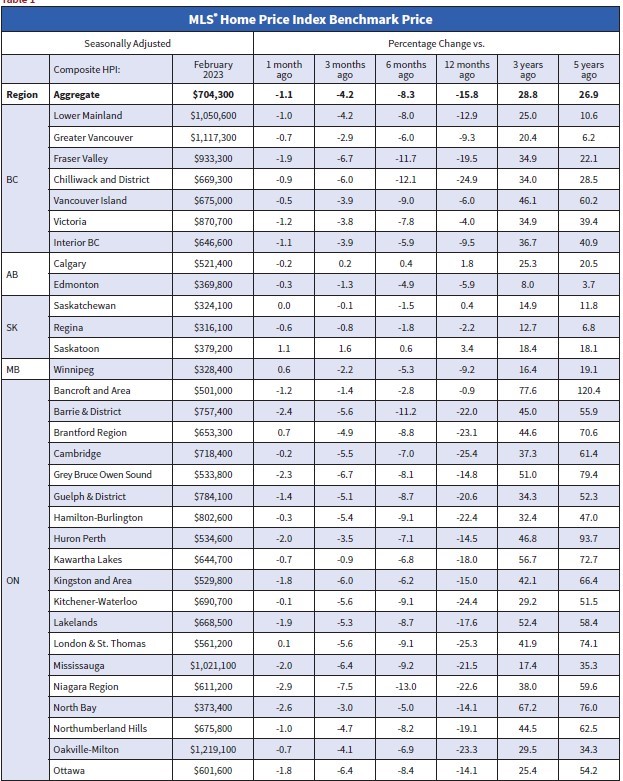
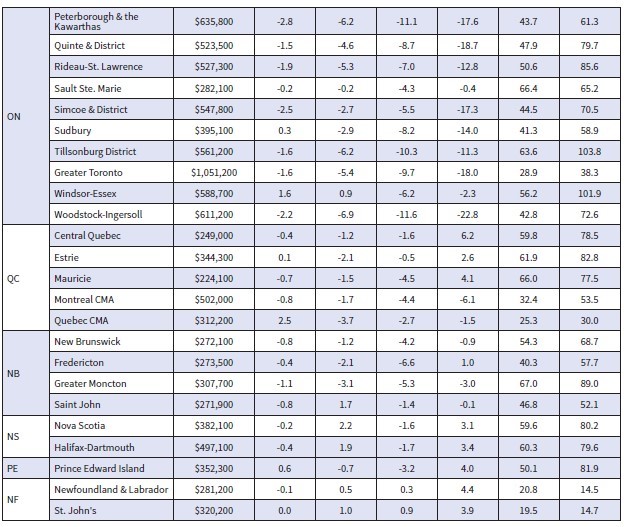
 The Canadian Real Estate Association says home sales in February bounced 2.3% from the previous month. Homeowners and buyers were comforted by the guidance from the Bank of Canada that it would likely pause rate hikes for the first time in a year.
The Canadian Real Estate Association says home sales in February bounced 2.3% from the previous month. Homeowners and buyers were comforted by the guidance from the Bank of Canada that it would likely pause rate hikes for the first time in a year.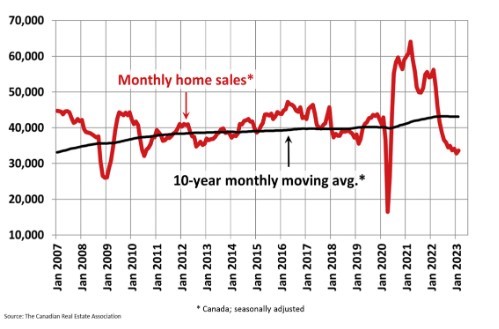
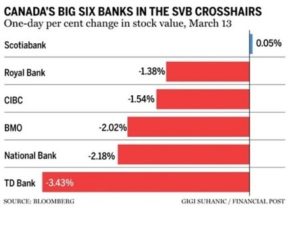
 ilicon Valley Bank (SVP) had a sterling reputation among the many tech start-ups it helped to finance. What brought SVB down was an old-fashioned bank run set off in 2021 by a series of bad decisions.
ilicon Valley Bank (SVP) had a sterling reputation among the many tech start-ups it helped to finance. What brought SVB down was an old-fashioned bank run set off in 2021 by a series of bad decisions.