Bank of Canada Will Not Be Happy With This Inflation Report
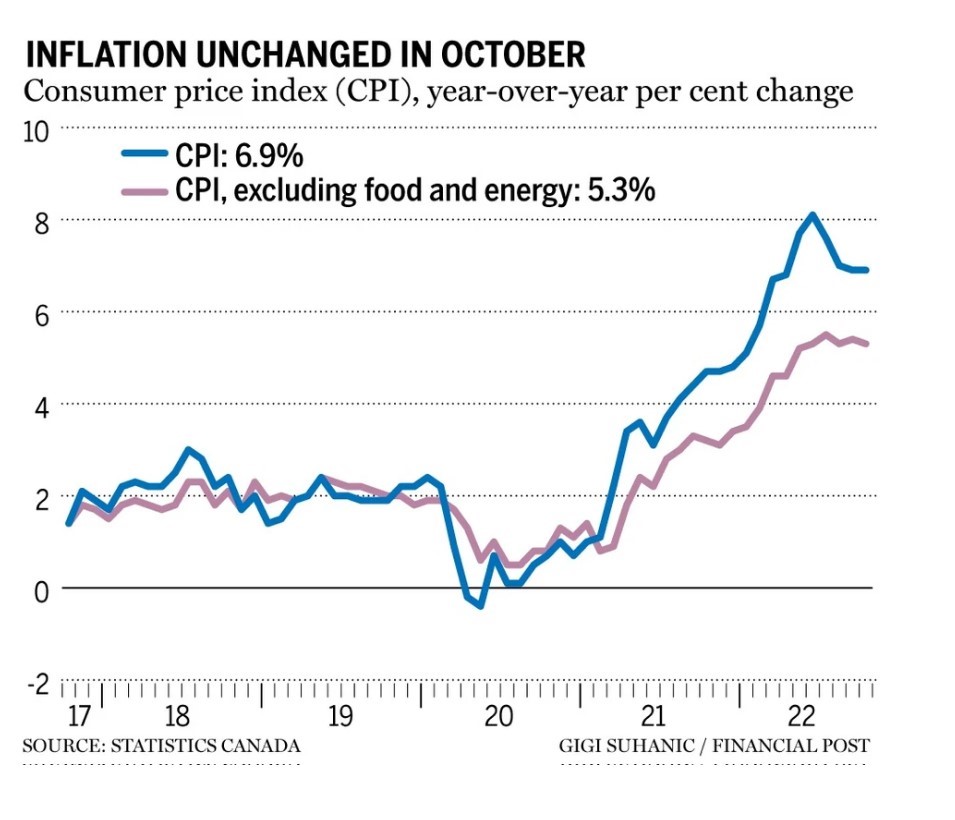
Not only did the headline CPI inflation rate stall at 6.9% last month, but the core CPI numbers remain stubbornly high. Food inflation–a highly visible component–edged down slightly. Still, prices for food purchased from stores (+11.0%) continued to increase faster year over year than the all-items CPI for the eleventh consecutive month. Bonds fell on the news, with Canada’s two-year yield rising to 3.877% at 8:43 a.m. Ottawa time, about 3.5 basis points (bps) higher than its level before the data release. The yield on 5-year Government of Canada bonds spiked temporarily on the release of these disappointing inflation data. This was in direct contrast to the US, which posted a better-than-expected inflation reading for October last week.
Less than two weeks after a stronger-than-expected jobs report, the inflation numbers continue to show the economy in overheated territory. Bank of Canada Governor Tiff Macklem has said that rates will need to continue to rise further while acknowledging the end of this tightening cycle is near.
Traders are pricing at least a 25 basis-point increase at the next policy decision on Dec. 7, with a 50-50 chance of a half percentage point hike. The central bank has increased borrowing costs by 3.5 percentage points since March, bringing the benchmark overnight lending rate to 3.75%.
A significant factor in the Bank’s decision process is the continued rise in wage inflation to a 5.6% annual pace in October. If inflation expectations remain robust, wage-price spiralling becomes a real threat.
Bottom Line
Price pressures might have peaked, but today’s data release will not be welcome news for the Bank of Canada. There is no evidence that core inflation is moderating despite the housing and consumer spending slowdown. The average of the Bank’s favourite measure of core inflation remains stuck at 5.3%. The central bank slowed reduced its rate hike at the October 26th meeting to 50 bps, and while some traders are betting the hike in December will be 25 bps, there is at least an even chance that the Governing Council will opt for an overnight policy target of 4.25%.
Inflation is still way above the Bank’s 2%-target level. Ultimately, it will take a higher peak interest rate to break the back of inflation. I expect the policy target to peak at about 4.5% in early 2023 and to remain at that level for an extended period despite triggering a mild recession in early 2023.

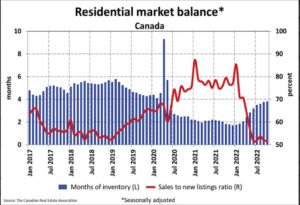
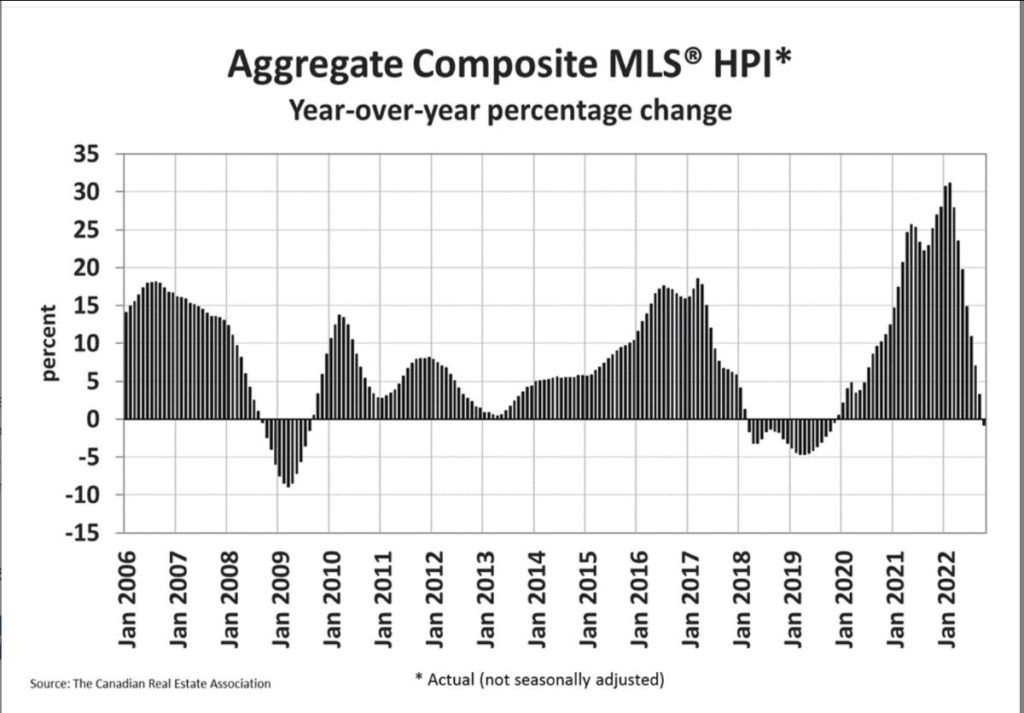
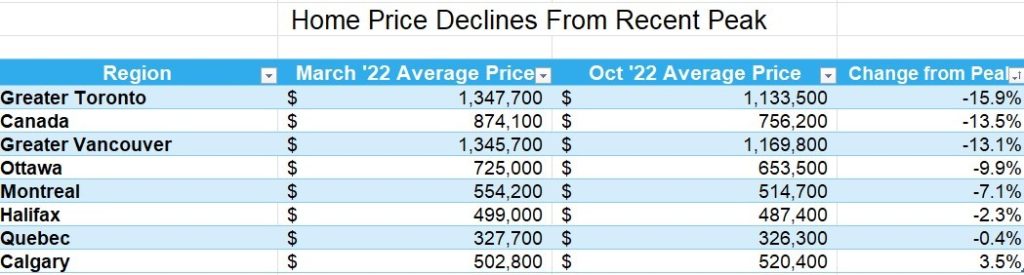
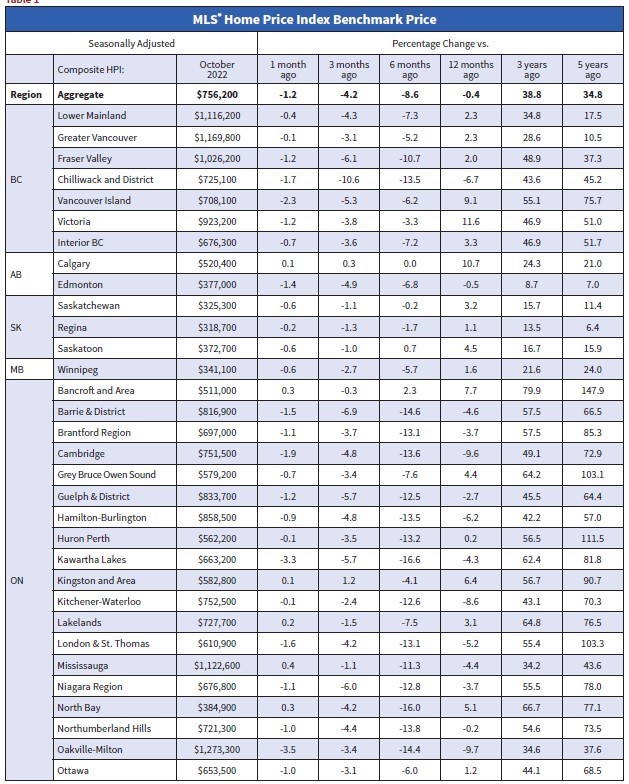
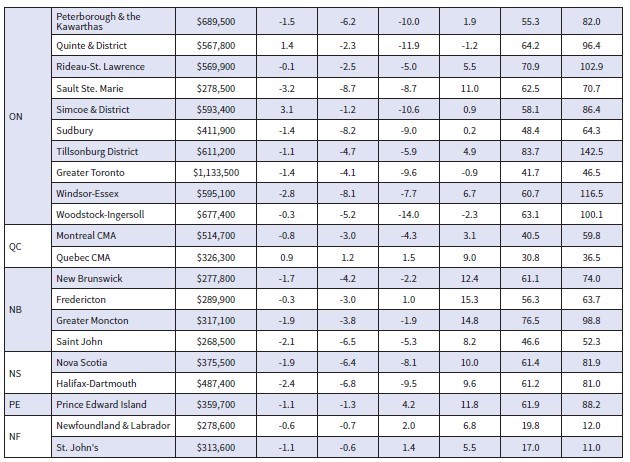
 Statistics released today by the Canadian Real Estate Association (CREA) show home sales were up 1.3% on a month-over-month basis in October. Still, monthly activity remained a whopping 36% below the October pace in 2021. The housing correction continues in response to the Bank of Canada’s massive rate hikes, but the speed of the correction is slowing.
Statistics released today by the Canadian Real Estate Association (CREA) show home sales were up 1.3% on a month-over-month basis in October. Still, monthly activity remained a whopping 36% below the October pace in 2021. The housing correction continues in response to the Bank of Canada’s massive rate hikes, but the speed of the correction is slowing.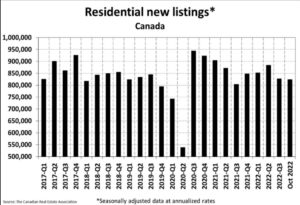
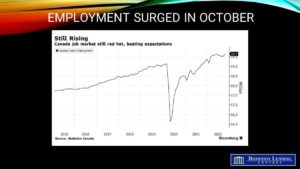
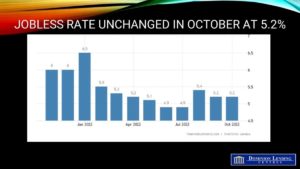
 Today’s Labour Force Survey for October was surprisingly strong, boosting wage inflation to an eye-popping 5.6% year-over-year pace. While good news for the economy, this is terrible news for the inflation fight–just when the Bank of Canada eased its foot on the brakes. The two-year and five-year Government of Canada bond yields spiked on the news, calling into question the Bank of Canada’s decision last week to trim the rate hike to 50 bps rather than the 75 bps that was expected. While one month’s data is not enough to draw too fine a point, this does call into question the assumption that fourth-quarter growth will be substantially less than 1%.
Today’s Labour Force Survey for October was surprisingly strong, boosting wage inflation to an eye-popping 5.6% year-over-year pace. While good news for the economy, this is terrible news for the inflation fight–just when the Bank of Canada eased its foot on the brakes. The two-year and five-year Government of Canada bond yields spiked on the news, calling into question the Bank of Canada’s decision last week to trim the rate hike to 50 bps rather than the 75 bps that was expected. While one month’s data is not enough to draw too fine a point, this does call into question the assumption that fourth-quarter growth will be substantially less than 1%.