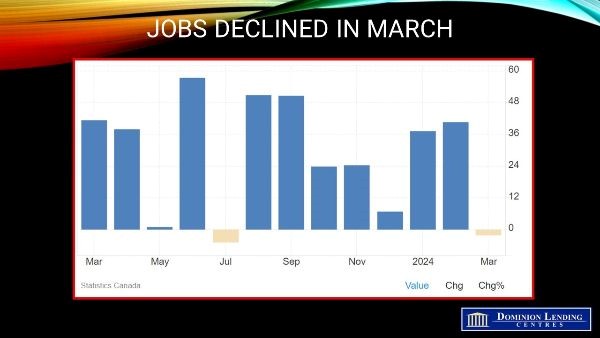
 The StatsCanada Labour Force Survey for March is much weaker than expected. Employment fell by 2,200, and the employment rate declined for the sixth consecutive month to 61.4%.
The StatsCanada Labour Force Survey for March is much weaker than expected. Employment fell by 2,200, and the employment rate declined for the sixth consecutive month to 61.4%.
Total hours worked in March were virtually unchanged but up 0.7% compared with 12 months earlier.
The details were similar to the headline: as full-time jobs dipped, total hours worked fell 0.3%, and only two provinces managed job growth. Among the type of worker, a 29k drop in self-employment was the primary source of weakness, while private sector jobs managed a decent 15k gain. The issue for the Bank of Canada is that wage gains are not softening even with a rising jobless rate. Average hourly wages actually nudged up to a 5.1% y/y pace, now more than two percentage points above headline inflation. With productivity barely moving, these 5% gains will feed into costs and threaten to keep inflation sticky.
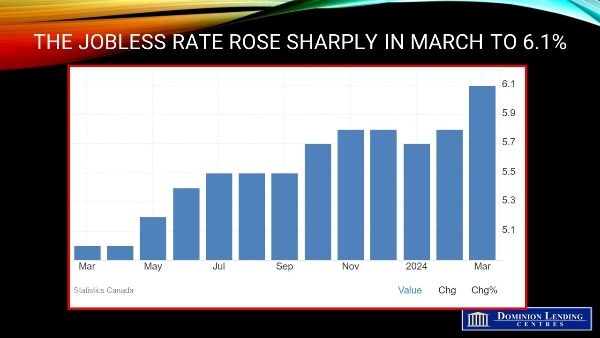
The unemployment rate in Canada jumped to 6.1% in March of 2024 from 5.8% in the earlier month, the highest since October of 2021, and sharply above market expectations of 5.9%. The result aligned with the Bank of Canada’s rhetoric that higher interest rates have a more significant impact on the Canadian labour market, strengthening the argument for doves in the BoC’s Governing Council that a rate cut may be due by the second quarter. The unemployed population jumped by 60,000 to 1.260 million, with 65% searching for jobs for over one month. Unemployment rose to an over-seven-year high for the youth (12.6% vs 11.6% in February) and grew at a softer pace for the core-aged population (5.2% vs 5%).In March, fewer people were employed in accommodation and food services (-27,000; -2.4%), wholesale and retail trade (-23,000; -0.8%), and professional, scientific, and technical services (-20,000; -1.0%). Employment increased in four industries, led by health care and social assistance (+40,000; +1.5%).
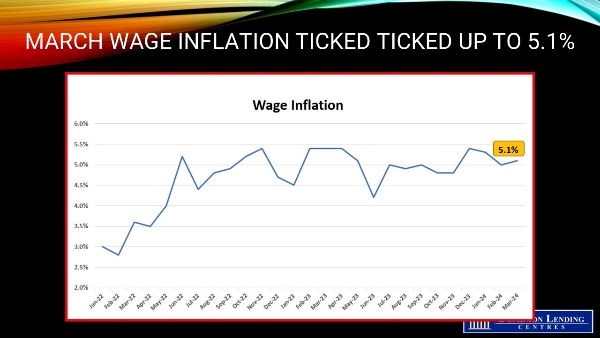
Average hourly wages among employees rose 5.1% (+$1.69 to $34.81) year over year in March, following growth of 5.0% in February (not seasonally adjusted). This is still too high for the Bank of Canada’s comfort.
Bottom Line
The central bank meets again on Wednesday, and a rate cut is unlikely. I still expect rate cuts to begin at the following meeting in June. The Canadian economy, though resilient, will suffer from rising mortgage costs as many mortgages come under renewal over the next two years. Delinquency rates have already risen. Moreover, the planned reduction in temporary residents will also slow economic activity.
With the US jobs market still booming, it is likely the BoC will begin cutting rates before the Fed.
