The Bank of Canada Won’t Like This Inflation Report
The Bank of Canada Won’t Like This Inflation Report
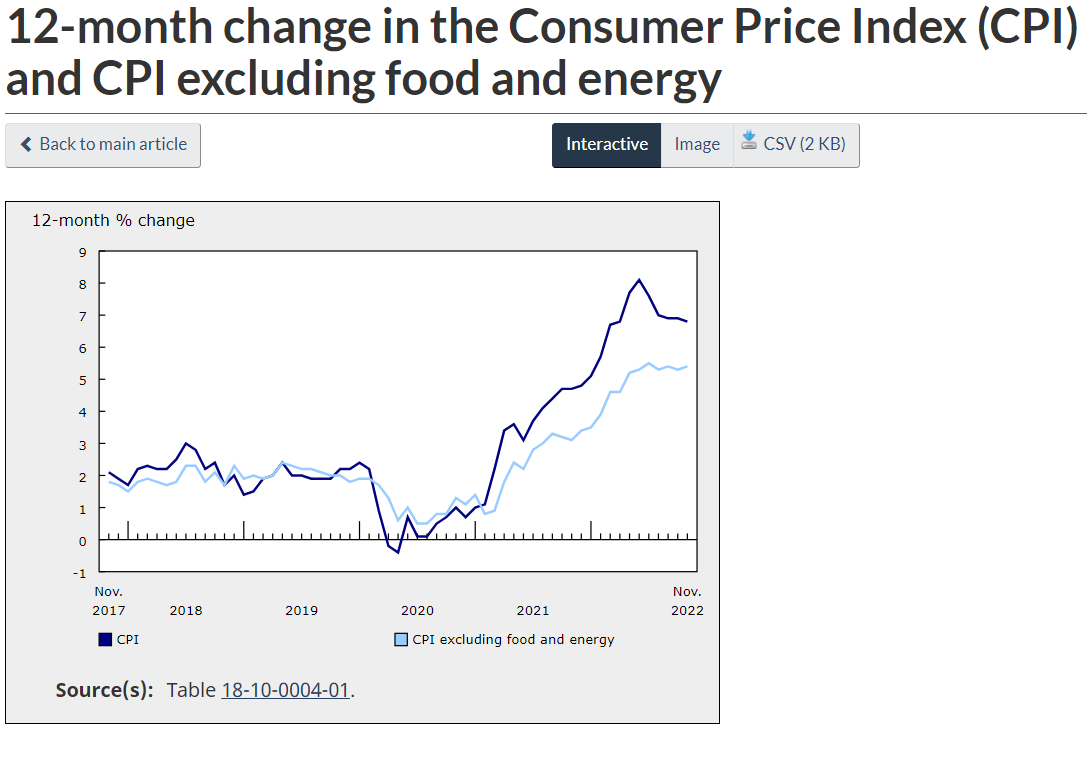
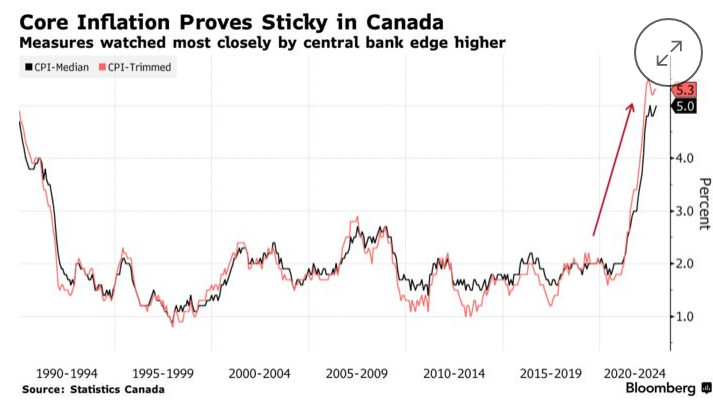
November’s CPI inflation rate fell only one tick to 6.8%, despite gasoline prices falling. This follows a two-month reading of 6.9%. Excluding food and energy, prices rose 5.4% yearly last month, up from 5.3% in October. Critical gauges of underlying price pressure were mixed but continued to creep higher. The all-important three-month trend in Core CPI edged to a 4.3% annualized rate from 4.0% the month before.
This is not good news and does nothing to assuage the central bank’s concerns about inflation. Price pressures remain stubbornly high, even as the economy slows and higher borrowing costs start to curb domestic demand.
Slower price growth for gasoline and furniture was partially offset by faster mortgage interest cost and rent growth. Headline inflation fell just one tick to 6.8% following two months at 6.9%, and core inflation remains sticky.
Digging into the still-strong core results revealed some new areas of concern. After years of helping hold back inflation, cellular services rose 2.0% y/yon “fewer promotions,” while rent took a big step up and is now at a 30-year high of 5.9% y/y (from 4.7% last month). Mortgage interest costs are another driving force, rising 14.5%, the most significant increase since February 1983. Just six months ago, they were still below year-ago levels. The transition from goods-led to services-driven inflation continues apace, with services prices up 5.8% y/y, or double the pace a year ago.
Prices for food purchased from stores rose 11.4% yearly, following an 11% gain in October.
Bottom Line
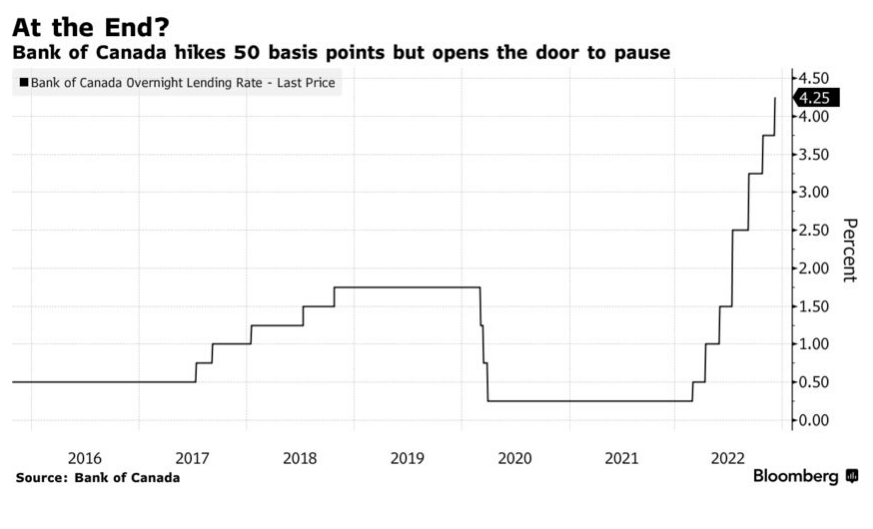
Before today’s report, traders were pricing in a pause at the next policy decision, with a possibility of a 25 basis-point hike. Barring an excellent inflation report for December, another rate hike is likely on January 25, likely a 25 bp hike. Given what’s happened in the first three weeks of this month, there is a good chance that the almost 14% drop in gasoline prices (compared to a 4% decline in December a year ago) could pull this month’s headline inflation down to 6.5%. However, many components of core inflation continue to rise.
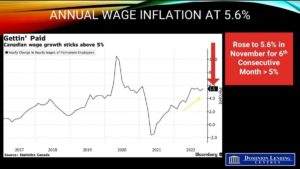
While the BoC will slow the rate hikes in 2023, at least two or three more hikes are still possible, with no rate cuts likely next year. Remember, wage inflation is running at 5.6% y/y, and wage negotiations are getting more aggressive.
Dr. Sherry Cooper | Chief Economist, Dominion Lending Centres

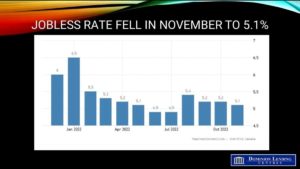
 Today’s Labour Force Survey for November will do little to assuage the Bank of Canada’s concern about inflation. While employment growth slowed to 10,100 net new jobs–down sharply from October’s reading–the report’s underlying details point to excess labour demand and rising wages. This is compounded by Monday’s data release showing that the Canadian economy grew by 2.9%, double the rate expected by the Bank of Canada. Everyone expects a slowdown in the current quarter and a modest contraction in the new year. However, excess demand is still running rampant in almost everything except housing.
Today’s Labour Force Survey for November will do little to assuage the Bank of Canada’s concern about inflation. While employment growth slowed to 10,100 net new jobs–down sharply from October’s reading–the report’s underlying details point to excess labour demand and rising wages. This is compounded by Monday’s data release showing that the Canadian economy grew by 2.9%, double the rate expected by the Bank of Canada. Everyone expects a slowdown in the current quarter and a modest contraction in the new year. However, excess demand is still running rampant in almost everything except housing.